文章目录[隐藏]

前言
参考的代码Mask_Rcnn
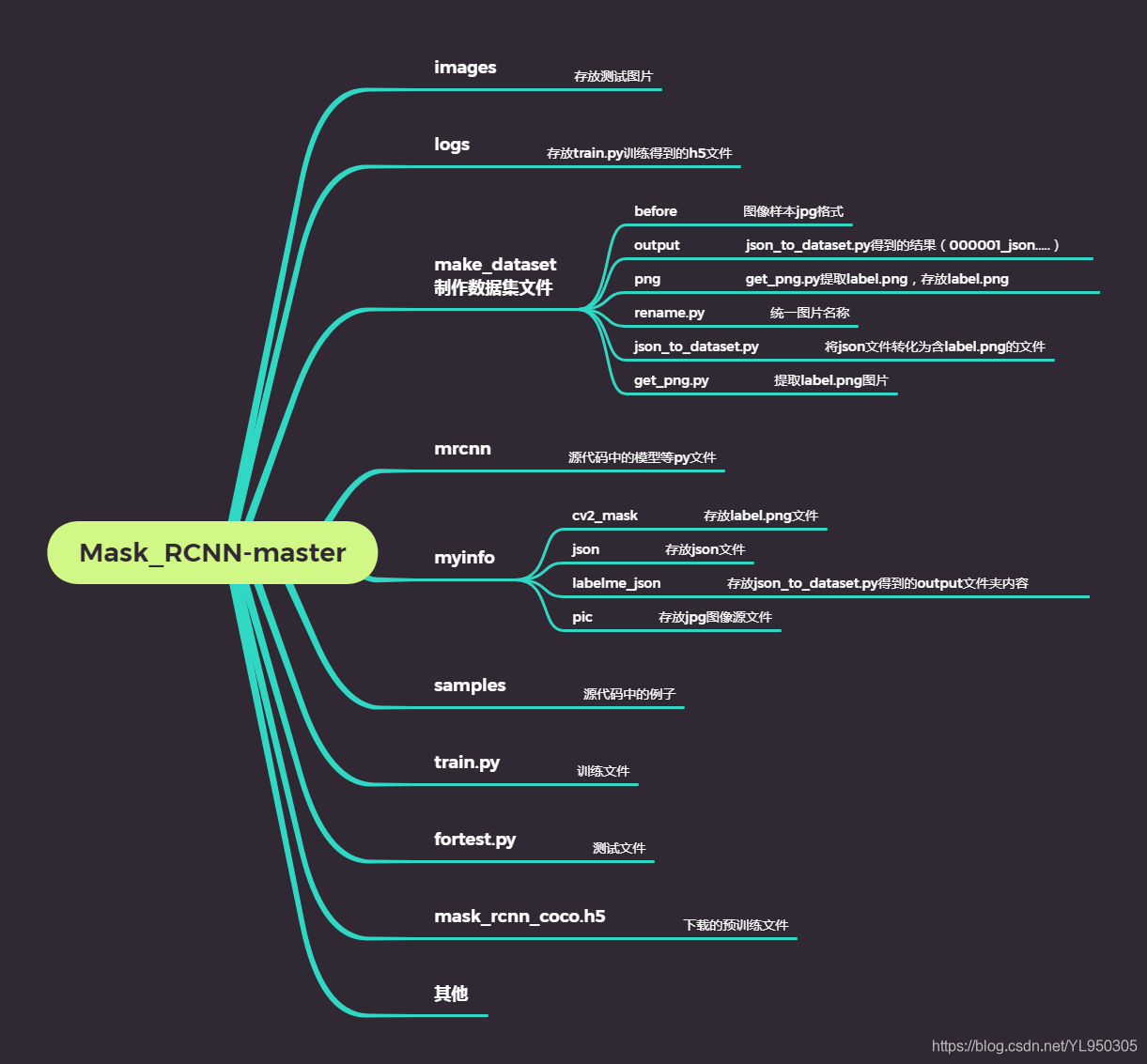
修改后的文件目录:
1. 数据集制作
1.1 数据集准备
1.1.1 样本
网上随便找的猫、狗、牛图片,有8张图(图名字和尺寸都需要统一格式),我用的数据集不是这个,目前项目没做完,所以就用这些图做个示范,主要用来记录这个过程,免得忘了!!!
1.1.2 rename.py 重命名
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/make_dataset/jpg"
# 改名字和后缀
filelist = os.listdir(path) #该文件夹下所有的文件(包括文件夹)
count=1
for file in filelist:
print(file)
for file in filelist: #遍历所有文件
Olddir=os.path.join(path,file) #原来的文件路径
if os.path.isdir(Olddir): #如果是文件夹则跳过
continue
filename=os.path.splitext(file)[0] #文件名
filetype=os.path.splitext(file)[1] #文件扩展名
# Newdir=os.path.join(path+str(count)+'.png') #用字符串函数zfill 以0补全所需位数
Newdir=os.path.join(path,str(count).zfill(6)+'.jpg')
os.rename(Olddir,Newdir)#重命名
count+=1
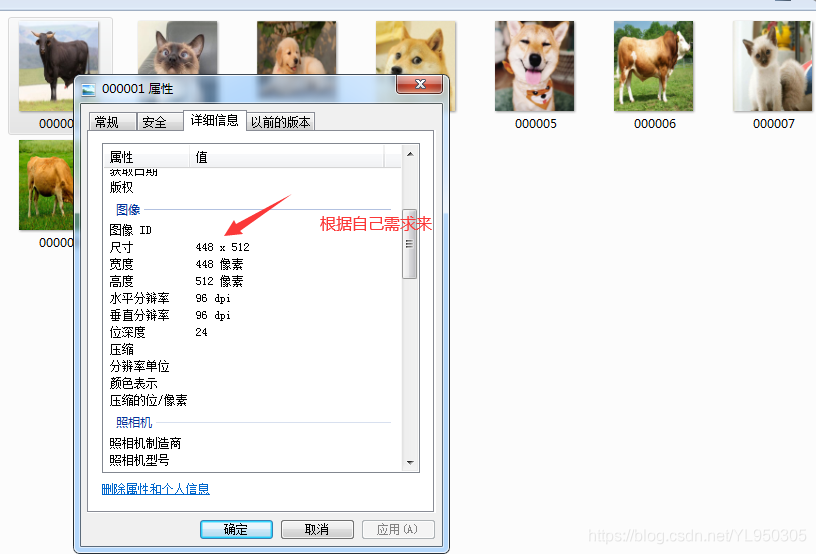
1.1.3 resize.cpp 统一图片的尺寸
可以用python的opencv,我是正好在做c++ opencv相关的东西,就用这个做了。
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
int main() {
String path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/make_dataset/jpg/"; //待处理图片文件夹地址
String dest = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/make_dataset/jpg/"; //处理后图片的保存地址
String savedfilename;
vector<cv::String> filenames;
glob(path, filenames); //opencv里面用来读取指定路径下文件名的一个很好用的函数
int num = filenames.size();
printf("The number of file is %d", num);
for (int k = 0; k < filenames.size(); k++)
{
Mat src = imread(filenames[k]);
resize(src, src, Size(448, 512));
int len = path.length();
savedfilename = dest + filenames[k].substr(len);
imwrite(savedfilename, src);
waitKey(30);
}
return 0;
}
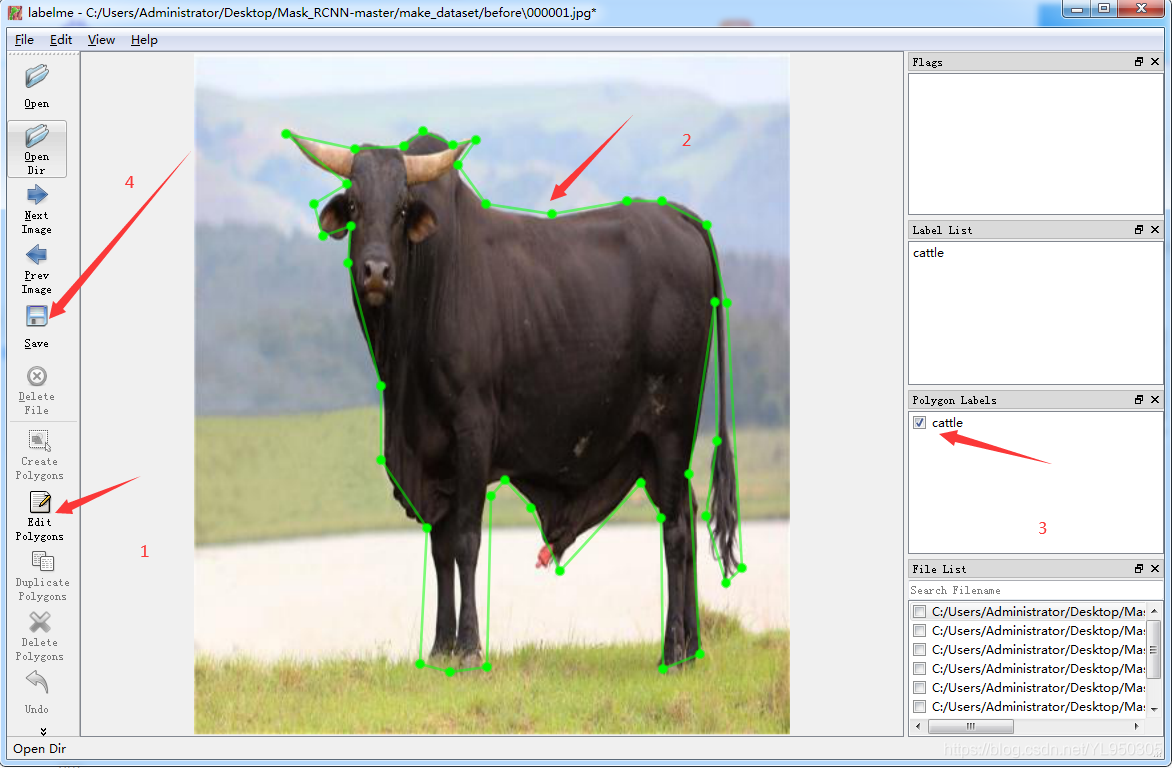
1.2 labelme标记得到json文件
安装和基本使用参考 labelme标记
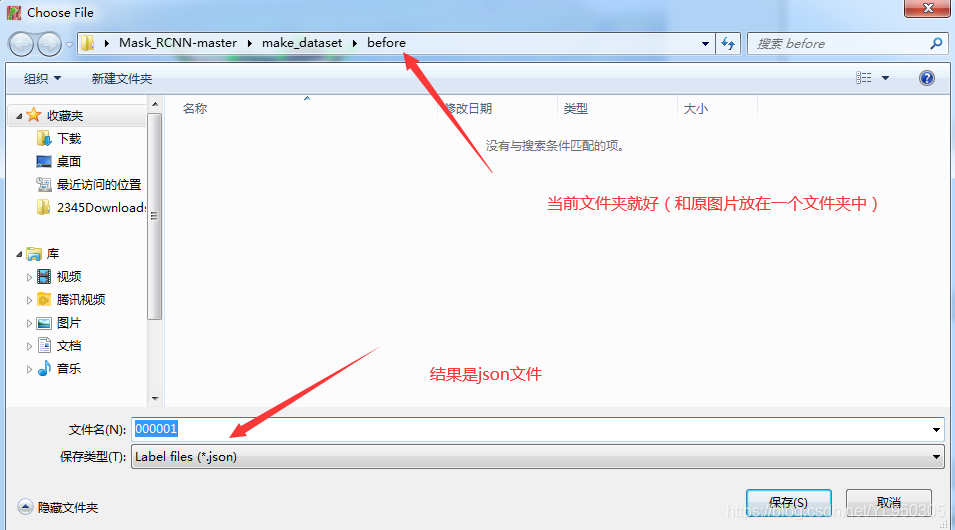
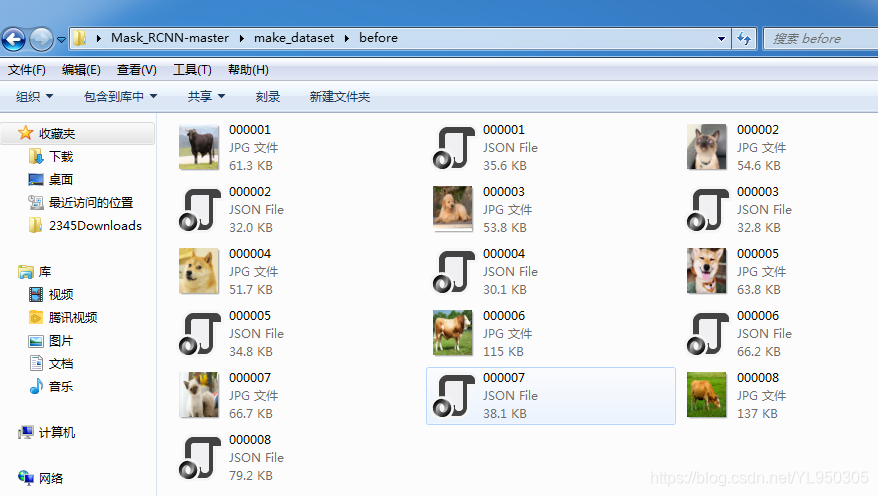
1.3 json_to_dataset.py将json文件转为label.png
import argparse
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import warnings
import PIL.Image
import yaml
# import draw
from labelme import utils
import base64
def main():
count = os.listdir("./before/")
for i in range(0, len(count)):
path = os.path.join("./before", count[i])
if os.path.isfile(path) and path.endswith('json'):
data = json.load(open(path))
if data['imageData']:
imageData = data['imageData']
else:
imagePath = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(path), data['imagePath'])
with open(imagePath, 'rb') as f:
imageData = f.read()
imageData = base64.b64encode(imageData).decode('utf-8')
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(imageData)
label_name_to_value = {'_background_': 0}
for shape in data['shapes']:
label_name = shape['label']
if label_name in label_name_to_value:
label_value = label_name_to_value[label_name]
else:
label_value = len(label_name_to_value)
label_name_to_value[label_name] = label_value
# label_values must be dense
label_values, label_names = [], []
for ln, lv in sorted(label_name_to_value.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]):
label_values.append(lv)
label_names.append(ln)
assert label_values == list(range(len(label_values)))
lbl = utils.shapes_to_label(img.shape, data['shapes'], label_name_to_value)
captions = ['{}: {}'.format(lv, ln)
for ln, lv in label_name_to_value.items()]
lbl_viz = utils.draw_label(lbl, img, captions)
out_dir = osp.basename(count[i]).replace('.', '_')
out_dir = osp.join(osp.dirname(count[i]), out_dir)
out_dir = osp.join("output",out_dir)
if not osp.exists(out_dir):
os.mkdir(out_dir)
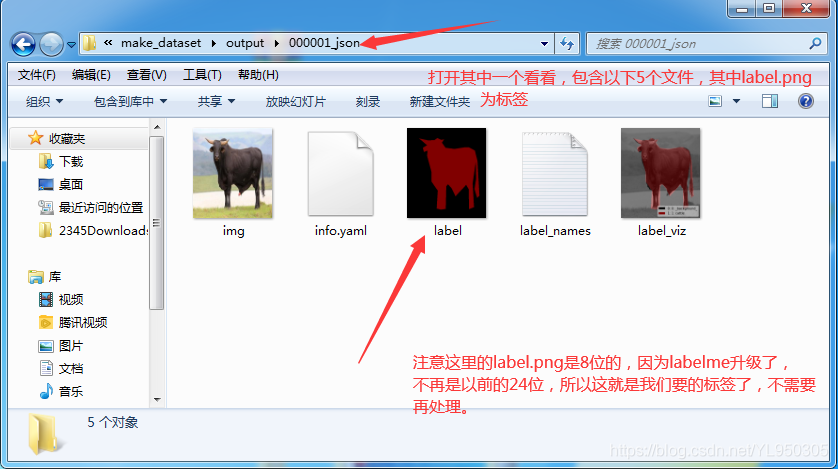
PIL.Image.fromarray(img).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'img.png'))
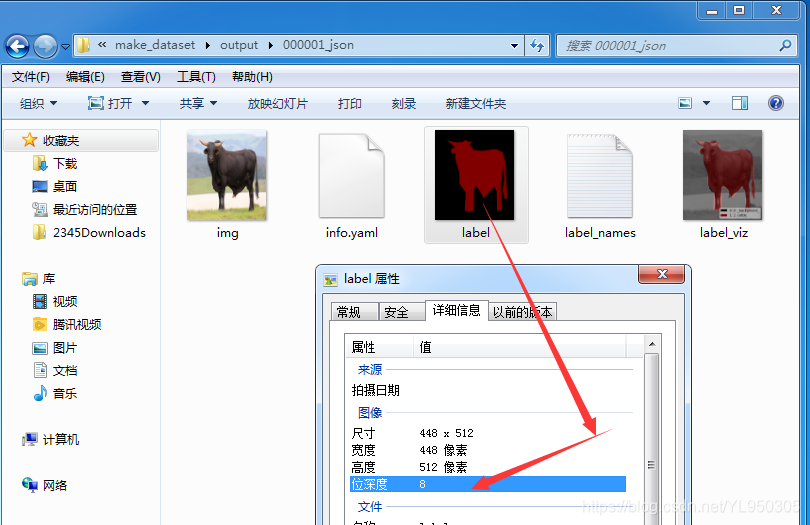
utils.lblsave(osp.join(out_dir, 'label.png'), lbl)
PIL.Image.fromarray(lbl_viz).save(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_viz.png'))
with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'label_names.txt'), 'w') as f:
for lbl_name in label_names:
f.write(lbl_name + '\n')
warnings.warn('info.yaml is being replaced by label_names.txt')
info = dict(label_names=label_names)
with open(osp.join(out_dir, 'info.yaml'), 'w') as f:
yaml.safe_dump(info, f, default_flow_style=False)
print('Saved to: %s' % out_dir)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
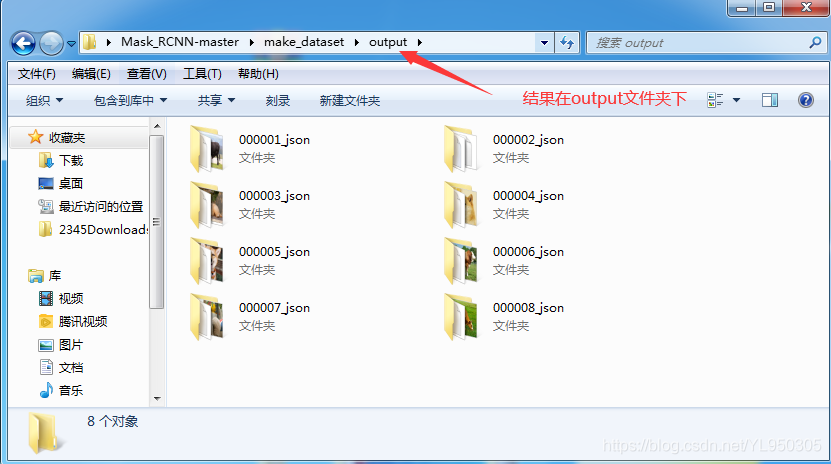
结果在output文件夹中
1.4 get_png.py 提取label.png
import os
import shutil
path = 'C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/make_dataset/output/'
file = os.listdir(path)
dirpath = 'C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/make_dataset/png/'
for eachfile in file:
if os.path.isdir(path+eachfile):
if os.path.exists(path+eachfile+'/label.png'):
(temp_name,temp_extention) = os.path.splitext(eachfile) #分离文件名与后缀
shutil.copy(path+eachfile+'/label.png',dirpath+temp_name.strip('_json')+'.png')
print(eachfile+' successfully moved')
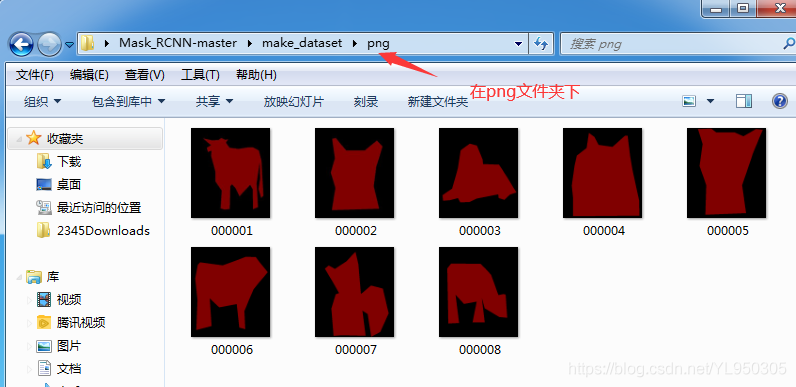
到这里数据集的制作基本完成,下面将做好的数据集按照mask rcnn的格式放在相应的文件夹中
1.5 制作mask rcnn数据集
在下载的代码目录下新建文件夹myinfo,以及4个子文件夹
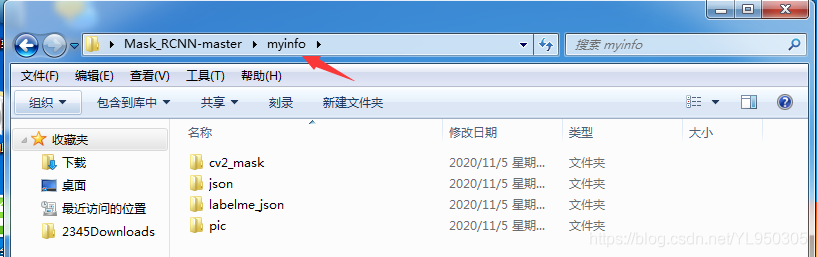
文件夹说明
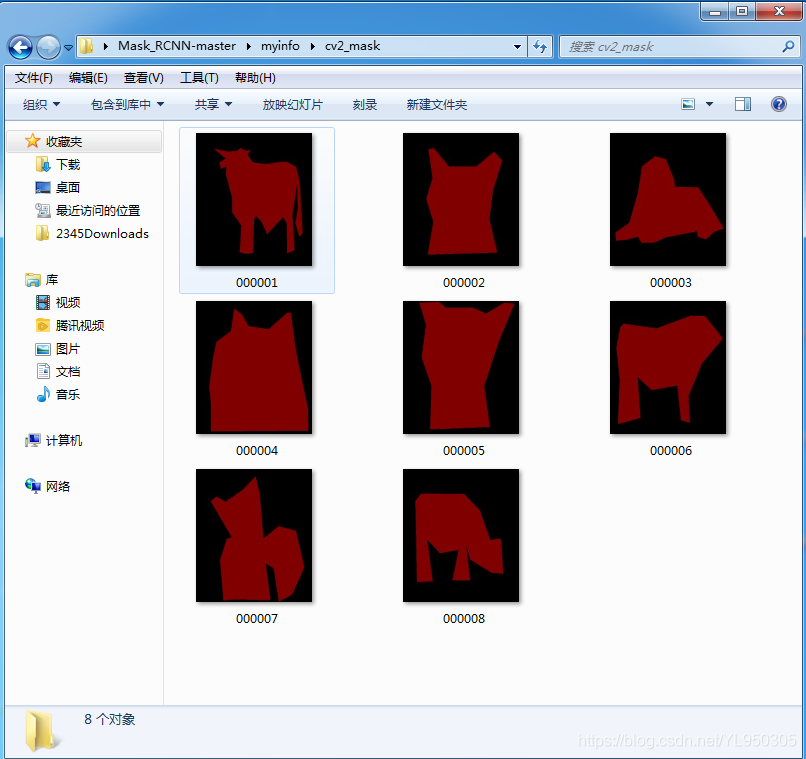
cv2_mask文件夹存放label.png文件
json文件夹存放json文件
labelme_json文件夹存放json_to_dataset.py得到的output文件夹内容
pic文件夹存放jpg图像源文件
2. 代码修改
2.1 训练文件train.py
在根目录下新建train.py,代码如下(源代码不知道在哪找的忘记了,下面是我改过之后的),等会再说怎么改。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import re
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from mrcnn.config import Config
# import utils
from mrcnn import model as modellib, utils
from mrcnn import visualize
import yaml
from mrcnn.model import log
from PIL import Image
# os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
# Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd()
# ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("../")
# Directory to save logs and trained model
MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs")
iter_num = 0
# Local path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
# Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed
if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH):
utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
class ShapesConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the toy shapes dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "shapes"
# Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each
# GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU).
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
# Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes
# Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side
# the large side, and that determines the image shape.
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 448
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 512
# Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8 * 6, 16 * 6, 32 * 6, 64 * 6, 128 * 6) # anchor side in pixels
# Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have
# few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs.
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 100
# Use a small epoch since the data is simple
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100
# use small validation steps since the epoch is small
VALIDATION_STEPS = 50
config = ShapesConfig()
config.display()
class DrugDataset(utils.Dataset):
# 得到该图中有多少个实例(物体)
def get_obj_index(self, image):
n = np.max(image)
return n
# 解析labelme中得到的yaml文件,从而得到mask每一层对应的实例标签
def from_yaml_get_class(self, image_id):
info = self.image_info[image_id]
with open(info['yaml_path']) as f:
temp = yaml.load(f.read())
labels = temp['label_names']
del labels[0]
return labels
# 重新写draw_mask
def draw_mask(self, num_obj, mask, image, image_id):
# print("draw_mask-->",image_id)
# print("self.image_info",self.image_info)
info = self.image_info[image_id]
# print("info-->",info)
# print("info[width]----->",info['width'],"-info[height]--->",info['height'])
for index in range(num_obj):
for i in range(info['width']):
for j in range(info['height']):
# print("image_id-->",image_id,"-i--->",i,"-j--->",j)
# print("info[width]----->",info['width'],"-info[height]--->",info['height'])
at_pixel = image.getpixel((i, j))
if at_pixel == index + 1:
mask[j, i, index] = 1
return mask
# 重新写load_shapes,里面包含自己的自己的类别
# 并在self.image_info信息中添加了path、mask_path 、yaml_path
# yaml_pathdataset_root_path = "/tongue_dateset/"
# img_floder = dataset_root_path + "rgb"
# mask_floder = dataset_root_path + "mask"
# dataset_root_path = "/tongue_dateset/"
def load_shapes(self, count, img_floder, mask_floder, imglist, dataset_root_path):
"""Generate the requested number of synthetic images.
count: number of images to generate.
height, width: the size of the generated images.
"""
# Add classes
self.add_class("shapes", 1, "cattle")
self.add_class("shapes", 2, "cat")
self.add_class("shapes", 3, "dog")
for i in range(count):
# 获取图片宽和高
print(i)
filestr = imglist[i].split(".")[0]
# print(imglist[i],"-->",cv_img.shape[1],"--->",cv_img.shape[0])
# print("id-->", i, " imglist[", i, "]-->", imglist[i],"filestr-->",filestr)
# filestr = filestr.split("_")[1]
mask_path = mask_floder + "/" + filestr + ".png"
yaml_path = dataset_root_path + "labelme_json/" + filestr + "_json/info.yaml"
print(dataset_root_path + "labelme_json/" + filestr + "_json/img.png")
cv_img = cv2.imread(dataset_root_path + "labelme_json/" + filestr + "_json/img.png")
self.add_image("shapes", image_id=i, path=img_floder + "/" + imglist[i],
width=cv_img.shape[1], height=cv_img.shape[0], mask_path=mask_path, yaml_path=yaml_path)
# 重写load_mask
def load_mask(self, image_id):
"""Generate instance masks for shapes of the given image ID.
"""
global iter_num
print("image_id", image_id)
info = self.image_info[image_id]
count = 1 # number of object
img = Image.open(info['mask_path'])
num_obj = self.get_obj_index(img)
mask = np.zeros([info['height'], info['width'], num_obj], dtype=np.uint8)
mask = self.draw_mask(num_obj, mask, img, image_id)
occlusion = np.logical_not(mask[:, :, -1]).astype(np.uint8)
for i in range(count - 2, -1, -1):
mask[:, :, i] = mask[:, :, i] * occlusion
occlusion = np.logical_and(occlusion, np.logical_not(mask[:, :, i]))
labels = []
labels = self.from_yaml_get_class(image_id)
labels_form = []
for i in range(len(labels)):
if labels[i].find("cattle") != -1:
# print "car"
labels_form.append("cattle")
elif labels[i].find("cat") != -1:
# print "leg"
labels_form.append("cat")
elif labels[i].find("dog") != -1:
# print "well"
labels_form.append("dog")
class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s) for s in labels_form])
print(class_ids)
return mask, class_ids.astype(np.int32)
def get_ax(rows=1, cols=1, size=8):
"""Return a Matplotlib Axes array to be used in
all visualizations in the notebook. Provide a
central point to control graph sizes.
Change the default size attribute to control the size
of rendered images
"""
_, ax = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(size * cols, size * rows))
return ax
# 基础设置
dataset_root_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Mask_RCNN-master/myinfo/"
img_floder = dataset_root_path + "pic"
mask_floder = dataset_root_path + "cv2_mask"
# yaml_floder = dataset_root_path
imglist = os.listdir(img_floder)
count = len(imglist)
# train与val数据集准备
dataset_train = DrugDataset()
dataset_train.load_shapes(count, img_floder, mask_floder, imglist, dataset_root_path)
dataset_train.prepare()
# print("dataset_train-->",dataset_train._image_ids)
dataset_val = DrugDataset()
dataset_val.load_shapes(count, img_floder, mask_floder, imglist, dataset_root_path)
dataset_val.prepare()
# print("dataset_val-->",dataset_val._image_ids)
# Load and display random samples
# image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_train.image_ids, 4)
# for image_id in image_ids:
# image = dataset_train.load_image(image_id)
# mask, class_ids = dataset_train.load_mask(image_id)
# visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset_train.class_names)
# Create model in training mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Which weights to start with?
init_with = "coco" # imagenet, coco, or last
if init_with == "imagenet":
model.load_weights(model.get_imagenet_weights(), by_name=True)
elif init_with == "coco":
# Load weights trained on MS COCO, but skip layers that
# are different due to the different number of classes
# See README for instructions to download the COCO weights
# print(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True,
exclude=["mrcnn_class_logits", "mrcnn_bbox_fc",
"mrcnn_bbox", "mrcnn_mask"])
elif init_with == "last":
# Load the last model you trained and continue training
model.load_weights(model.find_last()[1], by_name=True)
# Train the head branches
# Passing layers="heads" freezes all layers except the head
# layers. You can also pass a regular expression to select
# which layers to train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=50,
layers='heads')
# Fine tune all layers
# Passing layers="all" trains all layers. You can also
# pass a regular expression to select which layers to
# train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10,
epochs=50,
layers="all")
2.2 train.py修改的部分
1. 第53行: NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes(根据自己的目标来,以这个为例除背景外,还有3类cattle、cat、dog)
2. 第57-58行: IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 448
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 512(图片大小)
3. 第121-124行: # Add classes
self.add_class("shapes", 1, "cattle")(修改第2和3参数,若还有更多的类,往下加)
self.add_class("shapes", 2, "cat")
self.add_class("shapes", 3, "dog")
4. 第163-171行:
if labels[i].find("cattle") != -1:
# print "car"
labels_form.append("cattle")
elif labels[i].find("cat") != -1:
# print "leg"
labels_form.append("cat")
elif labels[i].find("dog") != -1:
# print "well"
labels_form.append("dog")
还有更多类就继续往下加
4. 注意一点: 33行COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
这个h5文件需要提前下载放在根目录下,下载地址https://github.com/matterport/Mask_RCNN/releases/download/v2.0/mask_rcnn_coco.h5
运行train.py,训练过程如下,看到这个不要慌,结果没问题,我用其他数据集测试过。
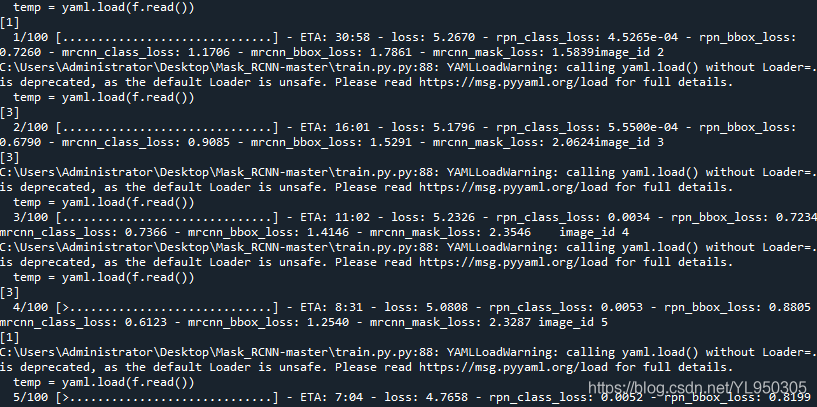
训练完成后在log文件夹中得到训练好的h5文件
2.3 测试文件fortest.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import skimage.io
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import time
from mrcnn.config import Config
from datetime import datetime
# Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd()
# Import Mask RCNN
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # To find local version of the library
from mrcnn import utils
import mrcnn.model as modellib
from mrcnn import visualize
# Import COCO config
# sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "samples/coco/")) # To find local version
# from samples.coco import coco
# Directory to save logs and trained model
MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs")
# Local path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR ,"shapes20201106T1424/mask_rcnn_shapes_0001.h5")
# Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed
if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH):
utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
print("cuiwei***********************")
# Directory of images to run detection on
IMAGE_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "images")
class ShapesConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the toy shapes dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "shapes"
# Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each
# GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU).
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
# Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes
# Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side
# the large side, and that determines the image shape.
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 448
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 512
# Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8 * 6, 16 * 6, 32 * 6, 64 * 6, 128 * 6) # anchor side in pixels
# Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have
# few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs.
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 100
# Use a small epoch since the data is simple
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100
# use small validation steps since the epoch is small
VALIDATION_STEPS = 50
#import train_tongue
#class InferenceConfig(coco.CocoConfig):
class InferenceConfig(ShapesConfig):
# Set batch size to 1 since we'll be running inference on
# one image at a time. Batch size = GPU_COUNT * IMAGES_PER_GPU
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
config = InferenceConfig()
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference", model_dir=MODEL_DIR, config=config)
# Create model object in inference mode.
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference", model_dir=MODEL_DIR, config=config)
# Load weights trained on MS-COCO
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True)
# COCO Class names
# Index of the class in the list is its ID. For example, to get ID of
# the teddy bear class, use: class_names.index('teddy bear')
class_names = ['BG', 'cattle', 'cat', 'dog']
# Load a random image from the images folder
file_names = next(os.walk(IMAGE_DIR))[2]
image = skimage.io.imread("./images/000001.jpg")
a=datetime.now()
# Run detection
results = model.detect([image], verbose=1)
b=datetime.now()
# Visualize results
print("shijian",(b-a).seconds)
r = results[0]
visualize.display_instances(image, r['rois'], r['masks'], r['class_ids'],
class_names, r['scores'])
2.4 fortest.py修改
1. 第30行:COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR ,"shapes20201105T1522/mask_rcnn_shapes_0001.h5")
h5路径和名字需要改,根据log文件夹下的路径改
2. 第54行: NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes
3. 第58-59: IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 448
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 512
4.第96行: class_names = ['BG', 'cattle', 'cat', 'dog']
5. 第99行: image = skimage.io.imread("./images/000001.jpg") (修改自己需要测试图片的路径)
运行fortest.py文件,结果如下:
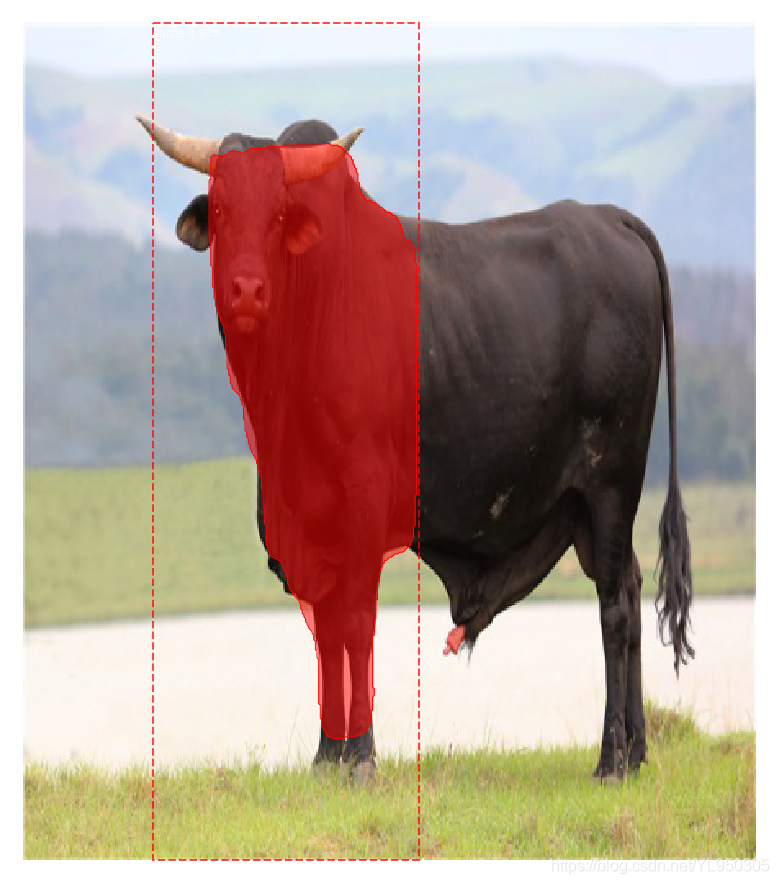

结果不好的原因是我只训练了一个epoch,然后图片样本只有8张,只是做个示范。
总结
记录点点滴滴
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「没得感情的吃货」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/YL950305/article/details/109527133









暂无评论